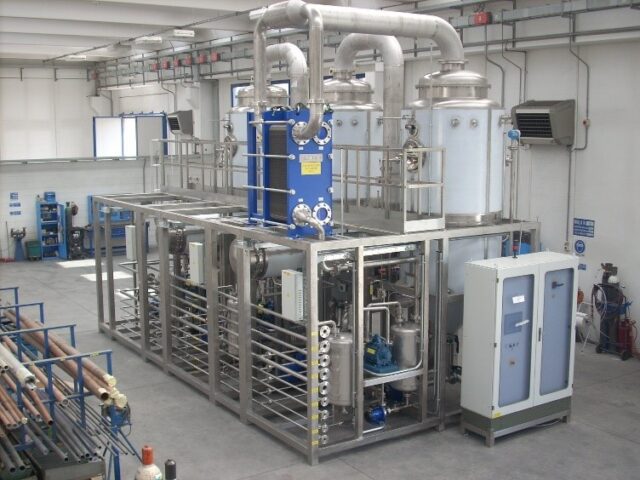
Distillation is a water purification process that utilizes the principles of evaporation and condensation to separate impurities from water. Distillation is one of the oldest techniques for treating water and continues to be utilized in modern times, although it is not frequently used as a method of household water purification.
The distillation process begins by heating the water in a container. As the water temperature rises, it eventually reaches its boiling point, causing the water molecules to transition into steam. This steam leaves various contaminants and impurities, such as salt, minerals, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and many organic compounds1.
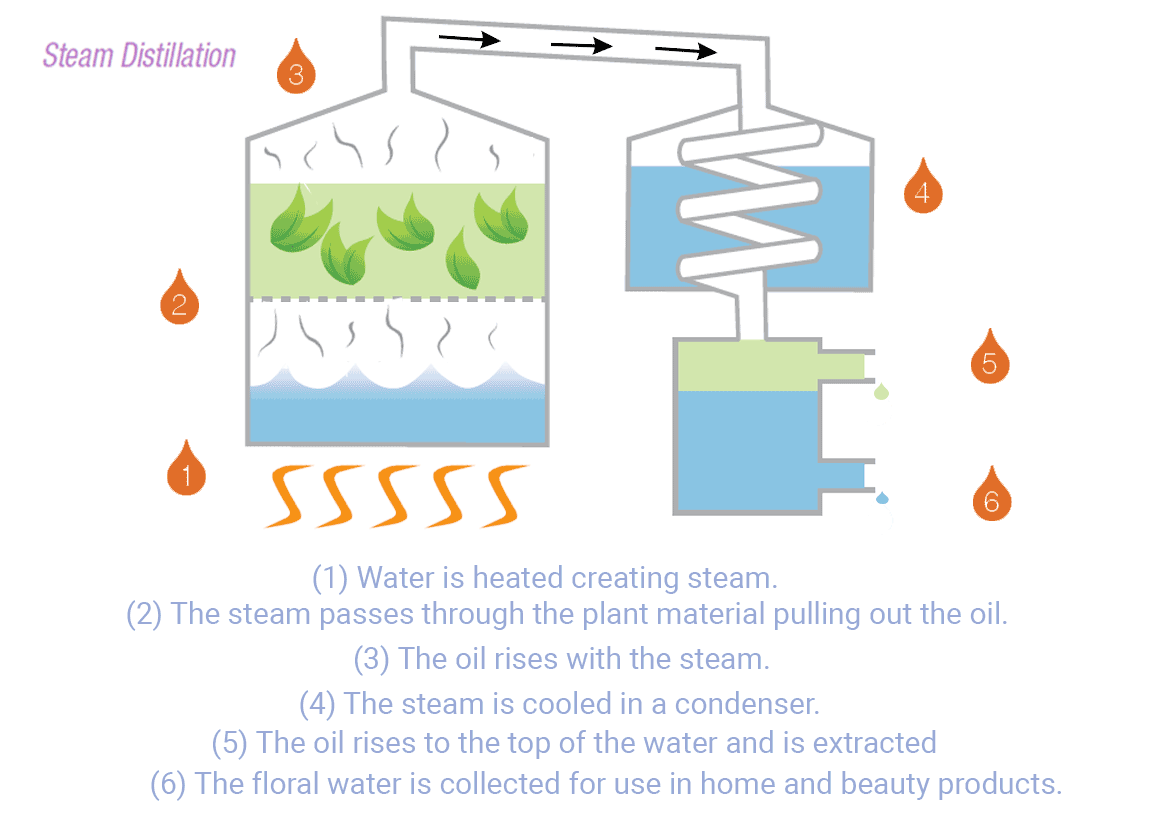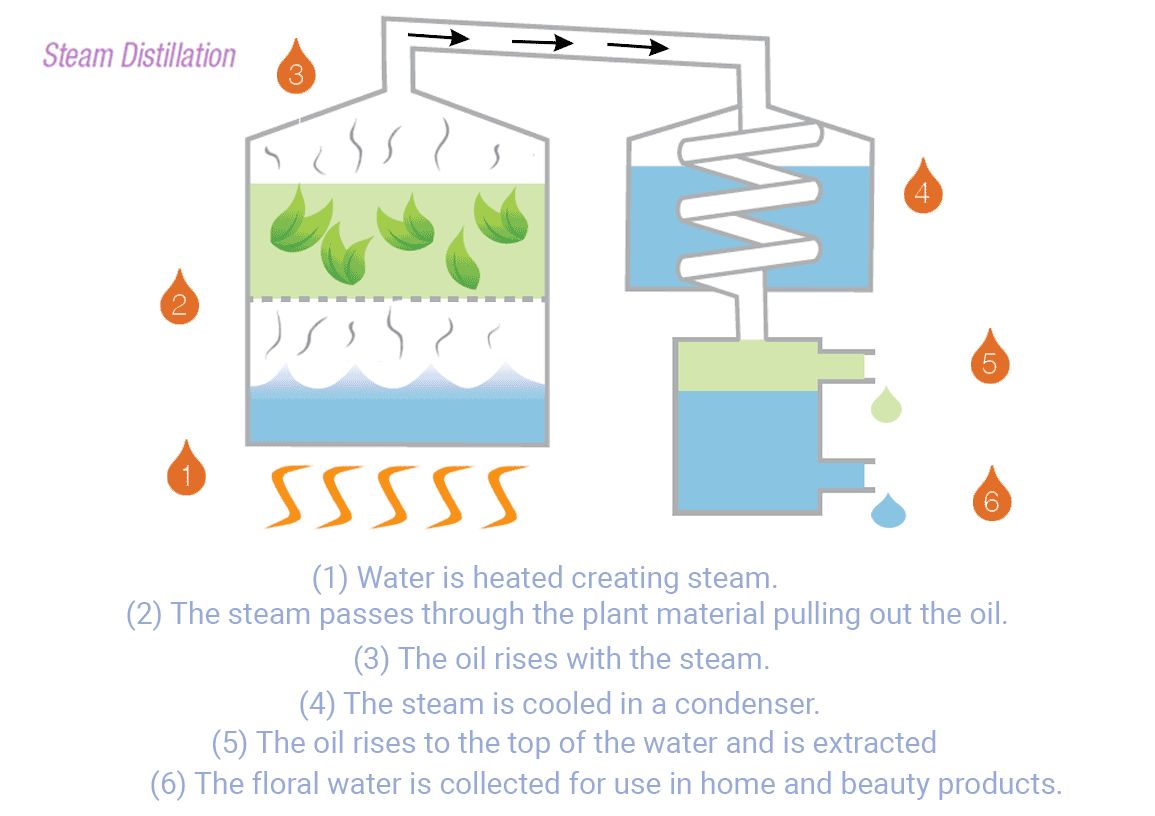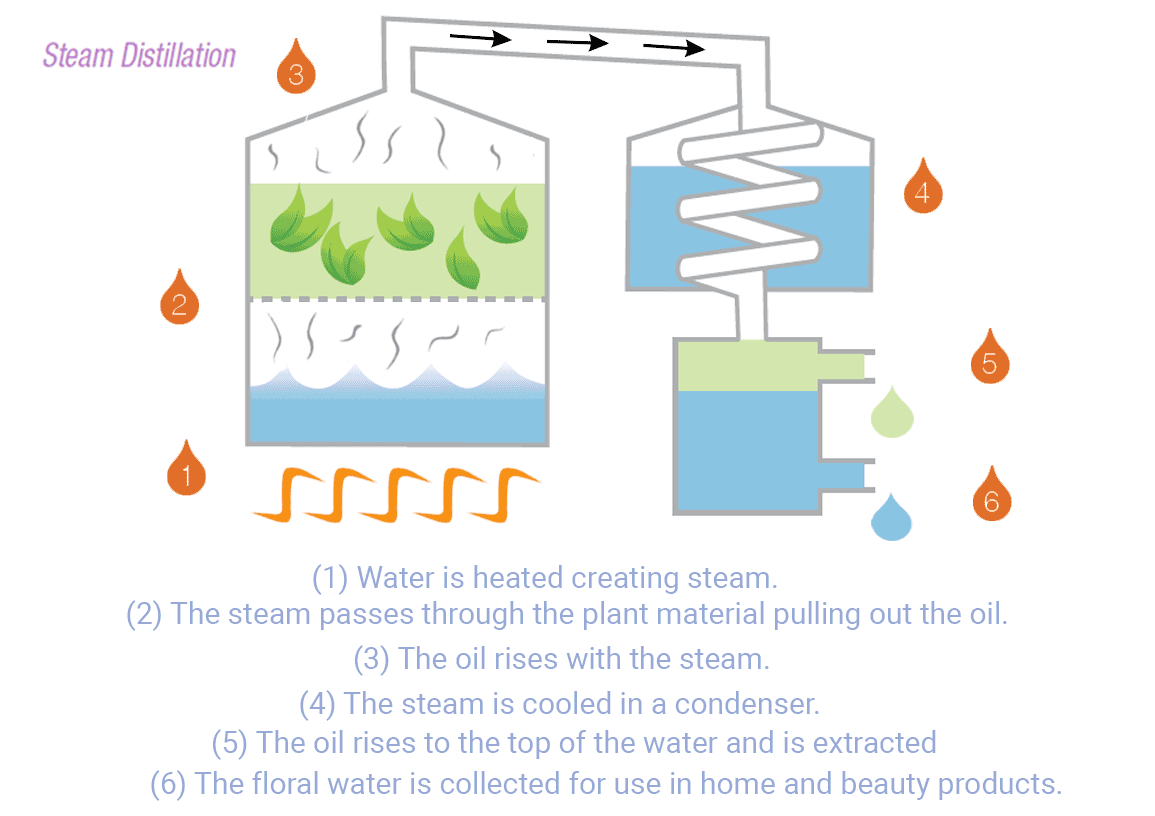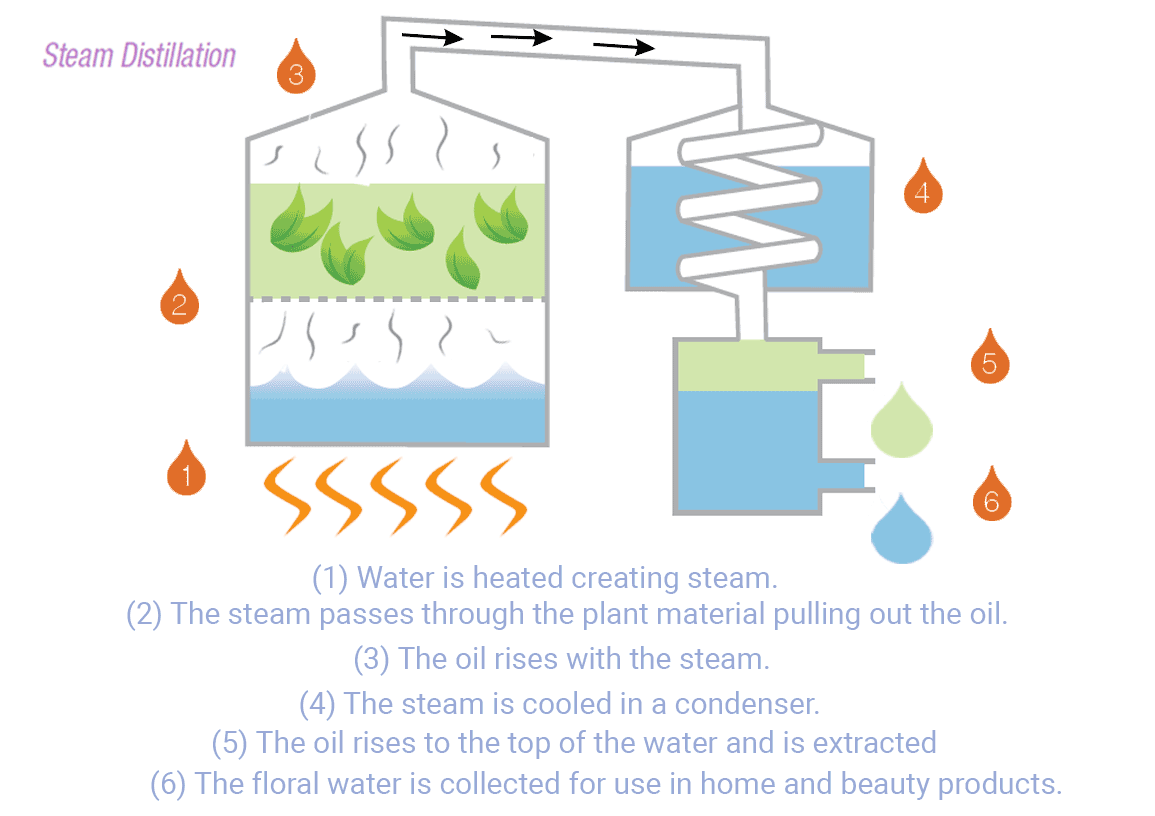
The steam flow enters a cooling system to be condensed back into liquid water. The condenser is designed to rapidly cool down and collect the water in a separate container1. This water can be utilized for household use, commercial, and industry in areas with limited access to fresh water.
Distillation can be adapted to various scales and applications despite its process requiring energy to heat the water and cool the steam, which can make it energy-intensive compared to some other purification methods. Additionally, certain volatile organic compounds might still be carried over into the distillate if not properly controlled. Although, distillation remains a reliable and widely employed method for obtaining high-quality purified water.
Source: